 Thicken
Thicken
Bodies: Thicken Main Page
The thicken option is somewhat unique to the InStep Studio application in that it is specifically intended to be used for cases where 3D scan (or other)
data has been loaded but a 'back-side' is missing. Frequently, this may be scan data taken with a laser scan on a fixed platform (therefore only
the front of the object was scanned) or similar. In this case and due to the (frequently) jagged edge that is formed around an otherwise shallow
shape, it is not possible - or only with complications - to close the hole formed by the sheet boundary:
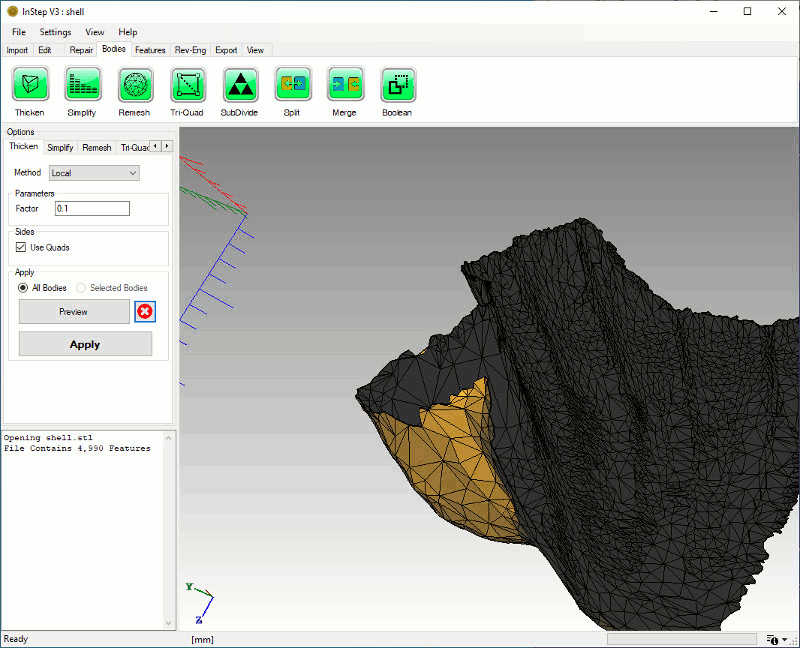 Shell Body
Shell Body
 Simplify
Simplify
Bodies: Simplify Main Page
The Simplify tool reduces the number of faces by collapsing or removing edges and facets.
Different algorithms are available that will either behave in an iterative way and consider facets that have a
smaller impact on the overall topology than others or work on a process to reduce the error in the final geometry compared to the initial body.
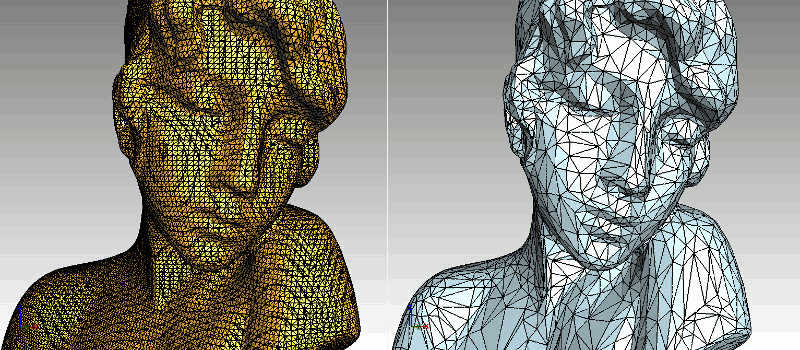 Mesh simplification (6.7% of original Body)
Mesh simplification (6.7% of original Body)
 Remesh
Remesh
Bodies: Remesh Main Page
The Remesh-ing tool allows the surface of the body to be re-tessellated (new triangles generated) that have a better quality / shape compared to the original
facets. This can aid in cases where the original data is either far too detailed, too coarse or generally contains a large number of slivers or similar issues
that other parts of the application can in some cases struggle with.
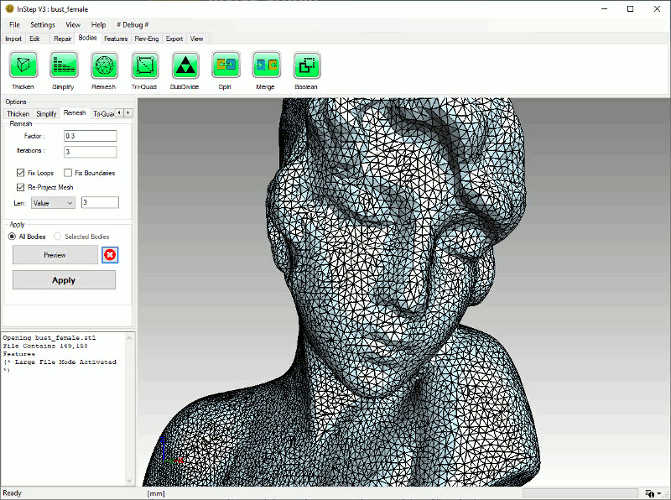 Re-Meshing to improve cell quality
Re-Meshing to improve cell quality
 Tri/Quad
Tri/Quad
Bodies: TriQuad Main Page
The Tri-Quad tool is a specialized helper that can convert between triangular and quadrilateral (aka Quad or 'square') facets. In general, almost all polygon representations
use triangles to represent the shape. However, in some cases, using Quad shapes is considered beneficial and the data is generally more compact. Likewise,
it is possible that the source data is in the form of quadrilateral facets and a triangular representation is required.
There are different methods, allowing conversion to a quad-dominant and, in most cases, pure-quad representation. Alternatively,
a method exists that guarantees a pure quad mesh at the expense of increasing the number of Quad elements (split-quad method).
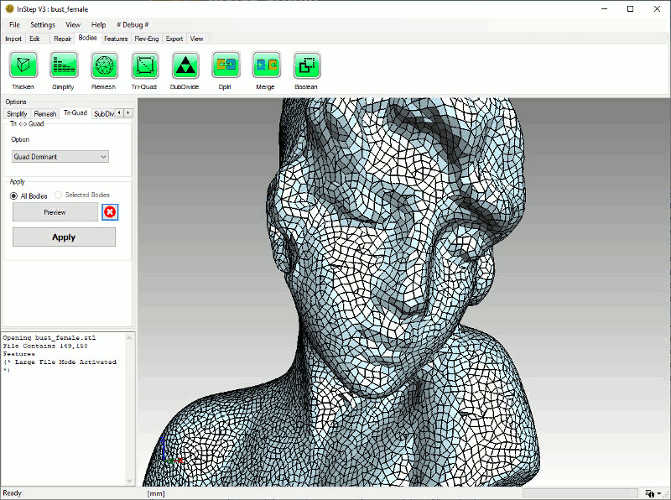 Tri to Quad Dominant (after remeshing)
Tri to Quad Dominant (after remeshing)
 SubDivide
SubDivide
Bodies: SubDivide Main Page
The Sub-Divide tool allows the data to be split so as to introduce a level of smoothness. This is generally not preferred (as more facets mean larger files), but in some cases
it may be beneficial to smooth out shapes in order to better represent the intent in perhaps the NURBS tool or similar. It is possible to process data in such a way as
to obtain a pure quadrilateral or pure triangular surface mesh.
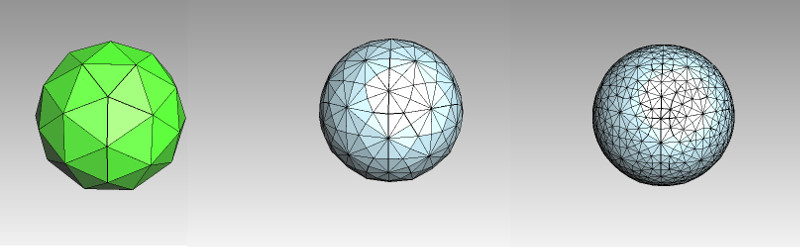 Smoothing by Sub-Division of facets
Smoothing by Sub-Division of facets
 Split
Split
Bodies: Split Main Page
The Split tool provides an easy way to break up data into groups based on surface continuity.
Depending on the Application Settings, the application will check whether the imported data is likely made
up of different parts that can be split during import and will ask whether to split the body into individual parts. In general, it is recommended to split data
as most of the application expects separate bodies to be processed one by one. In some cases however, the data should not be split as the imported facets represent
one continuous body and small gaps and discontinuities are errors, not separate surfaces.
Automatically checking and if possible, splitting data is generally recommended (you can reset this behavior from the Settings) but does take slightly longer during
import and may not always be the desired option. If an automatic split is performed on a body that should not have been split, the process can be reversed using the
Merge option (see below).
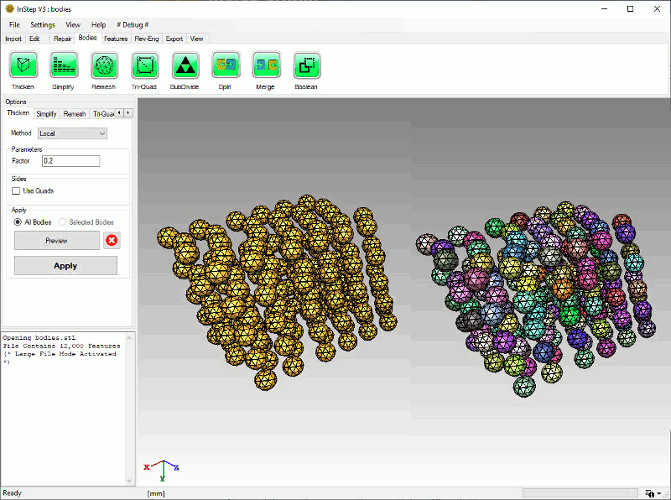 Original grouped data (left) and split bodies on right
Original grouped data (left) and split bodies on right
 Merge
Merge
Bodies: Merge Main Page
The reverse of the Split tool, the Merge tool combines Body data into a single set of data. Grouping of data in this way can be done on a All-Bodies basis or only
for those selected and thus allows for a larger group to be split and then selectively re-combined.
 Boolean
Boolean
Bodies: Boolean Main Page
Unlike the Merge tool which only groups data without modifying their content, the Boolean operations allow for data to be United, Subtracted or Intersected. The operation
of the Boolean methods regenerate a new set of surfaces using the corresponding functions to join/exclude voxels. It should be pointed out that the case of one body being fully
inside another is not well supported: the result is two bodies from the perspective of the application and any inside/outside information is lost when exported to STEP.
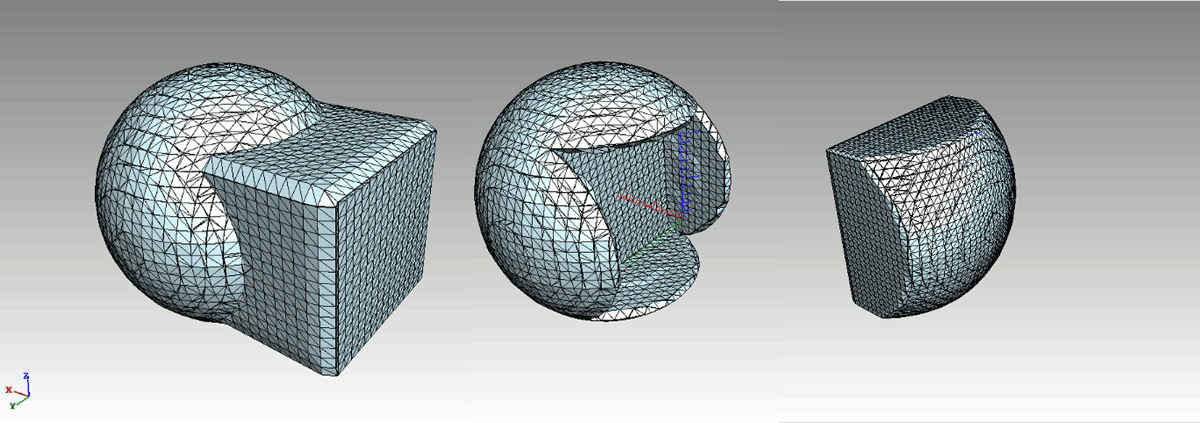 Boolean Unite, Subtract and Intersect operations
Boolean Unite, Subtract and Intersect operations